- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping

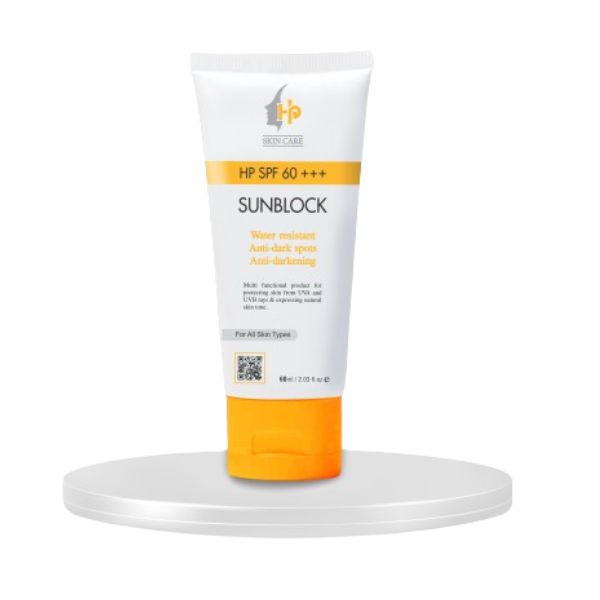
Sunblock For Skin
₨700.00 Original price was: ₨700.00.₨650.00Current price is: ₨650.00.
- Sunblock For Skin
Add to cart
Buy Now
Product Description
Sunblock For Skin
Sunblock For Skin also known as sunscreen, is a crucial product for protecting your skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Regular use of sunblock can help prevent sunburn, skin cancer, and premature aging of the skin.
Types of Sunblock:
- Physical (Mineral) Sunscreens:
- Ingredients: Typically contain zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide.
- How They Work: These create a physical barrier on the skin that reflects and scatters UV rays.
- Pros: Effective immediately upon application, less likely to cause skin irritation, and offer broad-spectrum protection against both UVA and UVB rays.
- Cons: Can leave a white cast on the skin, especially on darker skin tones, and may feel heavier.
- Chemical Sunscreens:
- Ingredients: Contain organic compounds like avobenzone, oxybenzone, octinoxate, and octocrylene.
- How They Work: Absorb UV rays and convert them into heat, which is then released from the skin.
- Pros: Tend to be lighter and more cosmetically elegant, often leaving no white cast.
- Cons: May cause irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals, and need to be applied 15-30 minutes before sun exposure to be effective.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Sunblock:
- SPF (Sun Protection Factor):
- SPF 15: Blocks about 93% of UVB rays.
- SPF 30: Blocks about 97% of UVB rays.
- SPF 50: Blocks about 98% of UVB rays.
- Higher SPF provides more protection, but no sunscreen can block 100% of UV rays. SPF 30 or higher is generally recommended for daily use.
- Broad-Spectrum Protection:
- Ensure the sunblock provides broad-spectrum protection, which means it protects against both UVA (which causes aging) and UVB (which causes burning) rays.
- Water Resistance:
- If you’re swimming or sweating, look for a sunblock labeled as water-resistant. These typically provide protection for 40 to 80 minutes in water before reapplication is needed.
- Skin Type:
- Sensitive Skin: Choose mineral sunscreens with fewer chemical ingredients.
- Oily or Acne-Prone Skin: Look for oil-free or non-comedogenic formulas.
- Dry Skin: Sunscreens with added moisturizers like hyaluronic acid or glycerin can help.
- Dark Skin Tones: Opt for sunscreens that leave no white cast, often found in chemical or tinted mineral sunscreens.
- Form:
- Creams: Ideal for dry skin and the face.
- Lotions: Suitable for larger areas of the body and most skin types.
- Gels: Better for hairy areas like the scalp or male chest.
- Sprays: Convenient but may not provide as even coverage; should be applied generously.
How to Use Sunblock Effectively:
- Application: Apply sunscreen generously to all exposed skin about 15-30 minutes before sun exposure.
- Reapplication: Reapply every two hours, or immediately after swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
- Amount: Use about a shot glass (1 ounce) of sunscreen to cover the entire body.
- Year-Round Use: Apply sunblock daily, even on cloudy days, as UV rays can penetrate through clouds and glass.
Additional Sun Protection Tips:
- Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, hats, and sunglasses.
- Seek shade during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
- Avoid tanning beds, which emit harmful UV radiation.
Using sunblock regularly is one of the most effective ways to maintain healthy skin and prevent skin damage. Choose a product that suits your skin type and lifestyle, and incorporate it into your daily routine for the best protection
Be the first to review “Sunblock For Skin” Cancel reply
Related products
-5%
₨2,100.00 Original price was: ₨2,100.00.₨1,995.00Current price is: ₨1,995.00.
Hp Glow Face Serum
-16%
₨1,000.00 Original price was: ₨1,000.00.₨845.00Current price is: ₨845.00.
HP Glow Day And Night Cream
-20%
₨1,000.00 Original price was: ₨1,000.00.₨800.00Current price is: ₨800.00.
ANTI ACNE CLEANSER
-15%
₨1,000.00 Original price was: ₨1,000.00.₨850.00Current price is: ₨850.00.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.